search engine marketing (SEM)
What is search engine marketing (SEM)?
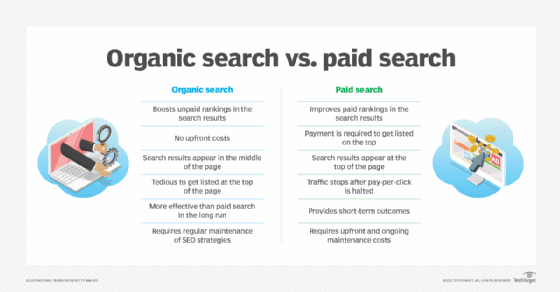
Search engine marketing (SEM) is a method of promotion and advertising to help companies' content rank higher among search engine traffic. Like search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing helps companies improve the way content is ranked by search engines.
SEM helps companies bring their products and services to the attention of audiences through paid search engine advertising. SEM is an online marketing strategy in which organizations buy targeted ad space at the top of search engine result pages (SERP). This approach is different from SEO, which focuses on optimizing content for search engine algorithms so the content ranks high on the SERP.
Google, Bing and Yahoo are the most popular search engines. Each uses an auction process to determine where SEM ads rank on their SERP.
SEO vs. SEM
SEO and SEM use many similar tactics; however, they are distinctly different methods of ranking high on a SERP.
SEO
SEO is the practice of structuring content so it ranks high in organic search results, which are the unpaid content listings on a results page. The key aspects of SEO include the following:
- It is based on the limited knowledge of the secret ranking factors, also known as signals, that search engines like Google use.
- SEO methods are constantly changing to keep pace with the evolving algorithms search engines use.
- SEO-driven results rank directly below paid searches.
- Successful SEO relies on creating useful, authoritative and trusted content. SEO practitioners take steps such as the following:
- increasing the number of external webpages linking to a page, also known as backlinks;
- identifying and adding relevant keywords to content;
- expanding trust signals based on website security, cumulative site traffic and user engagement; and
- ensuring the website provides a good user experience (UX).
SEM
SEM focuses largely on using paid advertising to increase traffic through services such as Google ads or Bing ads. The following are key aspects of SEM:
- It is based on keyword analysis. Marketing departments identify keyword terms that might draw users to a webpage. Like SEO practitioners, search engine marketers use keyword research analysis and tools to identify keyword phrases audiences are searching for. They then buy ad space on the results pages from the search engine provider for the search terms they want to target.
- SEM paid search results go at the top of the SERP.
- SEM benefits from webpages that are easy for web crawlers to scan and include trust signals such as linking to other websites.

How SEM works
Search engine marketers first identify keywords with large search volumes and then buy ad space on the SERPs for those keywords. These campaigns pay per click (PPC), which means the marketer pays the search engine provider every time a user clicks its ad. For organizations selling products and services, the revenue generated from customers buying products they access via the SEM ad should outweigh the cost of PPC.
SEM ads are placed at the top of a SERP, above the organic results generated by SEO. They appear similar to organic results and include the following characteristics:
- headlines or title tags;
- summaries of the webpage content, known as the meta description;
- calls to action, meaning text that inspires visitors to make a certain action, such as buying a product or subscribing to a service; and
- URL hyperlinks.
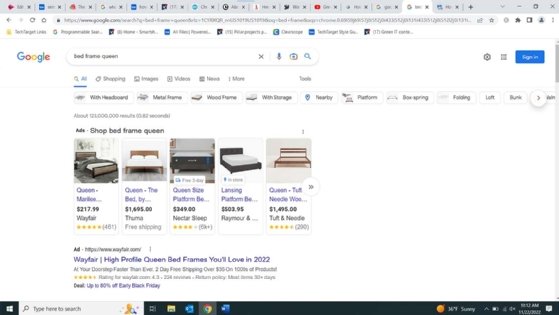
Importance of SEM
SEM marking strategies are important for the following reasons:
- Digital marketing. Online purchases are one of the most popular ways customers shop. SEM campaigns attempt to expand the reach of digital marketing by identifying and using keywords that will attract the people most likely to be interested in the marketer's product or service. Essentially, SEM campaigns target the most profitable keywords.
- High conversion rates. One of the biggest advantages of SEM marketing efforts is that they position an organization's product right in front of customers when they are ready to make a purchase. For example, by purchasing an ad for a product keyword -- "food processor," for example -- customers looking to buy a food processor online will see a company's product ad first. With SEM, there is a good chance that the visitors clicking on an ad want to make a purchase, increasing an organization's customer conversion rates and optimizing customers' purchase intent.
- Speed. An SEM strategy often drives increased traffic more quickly than SEO, which can require long periods of time to analyze keywords and shape content to SEO research. SEM puts products and services right in front of customers immediately by placing them at the very top of SERPs.
- PPC model. The PPC model, which is similar to the cost per engagement model, is a cost-effective strategy that enables organizations to only pay when their ad is clicked. Organizations can also control exactly how much they spend by setting a maximum cost per click (CPC) and daily budget.
- Increased organic rankings and trust signals. Increased traffic to a page through paid ads ultimately increases overall traffic to a page and enhances trust signals ranked by Google. If a product performs well enough through an SEM campaign, it can rank high on a SERP organically, making SEM no longer necessary.
- Segmentation. Besides keywords, SEM campaigns can control what geographic location, language and online behavior to target, ensuring they only reach the users that might be interested in their product or services.
- Deep insight. Tools like Google Analytics give organizations highly detailed reports on the state and evolution of their SEM campaigns in real time. This gives useful insights into how SEM campaign ads are performing, which helps organizations analyze how they could improve their campaign.
Disadvantages of SEM
SEM also has some downsides and challenges, including the following:
- Cost. Even with cost-effective models like PPC, SEM can become expensive over time, as organizations have to pay every time their ad is clicked on. With SEO, there are no click- and ranking-related costs.
- Competition. Depending on the campaign's target audience, buying ads and ensuring the top spot at the top of SERPs can become challenging and expensive. An increase in companies competing for the top ad spot is causing CPC and related costs to rise.
- Customer trust and ad blockers. Many customers don't enjoy or trust ads and block them with ad blockers. Ads can be seen as disruptive and less trustworthy than inbound marketing techniques, which generate organic search results.
SEM keyword research strategies
Successful SEM strategies depend on identifying and purchasing ad space on the most effective keywords and long-tail keyword phrases related to a product or service. SEM keyword research strategies are based on keyword intent, sometimes called searcher intent. Keyword intent refers to what action a user is likely to take when they search a specific keyword. SEM strategies focus on identifying and using keywords that are most likely to drive a user to make a purchase.
Several tools help marketers identify the most important keywords, including these six:
- Clearscope
- Google Ads Keyword Planner
- Google Trends
- Keyword Tool
- Semrush
- SpyFu
Successful keyword research can also help SEM marketers identify and avoid negative keywords. These are keywords that are unlikely to rank high on search engine results pages and attract potential customers.
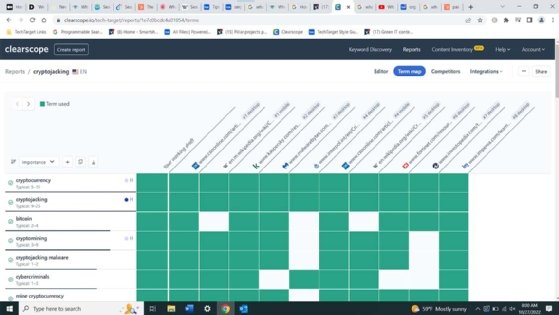
How ad auctions work
For Google, Bing and Yahoo, all ads must go through an auction process that takes place every time a user makes a search. For instance, the Google ad auction uses multiple factors to determine which ad goes at the top of the SERP -- including the quality score an ad gets on Google Ads, Google's pay-per-click advertising platform.
The SEM campaign with the biggest budget does not always get the top spot. Competitors with a lower bid can win ad space over organizations with higher bids if their content is more relevant. Also, some of the factors that determine organic search engine ranking also come into play in the Google auction, such as trust signals and web traffic.
Once an SEM campaign has identified the keywords to target, it can enter the auction for those keywords. Search engine auctions generally follows these four steps:
- Bidding. The SEM campaign enters the maximum amount it is willing to pay for a keyword.
- Quality score. Platforms like Google Ads grade the ad and the website hosting it based on the keywords used, the UX of the website, how useful the content on the ad's landing page is and ad assets, such as phone numbers and links that might be useful to visitors. Google also has quality thresholds that ads must meet to earn a specific ad rank.
- Context considerations. Because auctions happen every time a user makes a search, search engines like Google and Bing also consider contextual information in determining an ad's ranking. These include the searcher's physical location, search history, the time of the search, the device used to make the search, and other ads and organic search results on the page.
- Ad rank determined. An ad rank is awarded to the bidder. Because of all the metrics Google considers in addition to the price of the bid, the highest ad rank is not guaranteed to go to the highest bidder.
Creating an SEM campaign strategy
To create a successful SEM campaign strategy, marketers make use of a variety of strategies and tools, including the following:
- Keyword research. The first step in an SEM campaign is for an organization to identify the most effective keywords it wants to purchase ad space on. This can be done through the use of online keyword research tools. Research should also be done into competitors' ads and geo-marketing information about target audiences.
- Budget. Marketers create a budget for the ad campaign and set a maximum bid amount.
- Ad groups. An organization advertising several products or services might have to organize its products into multiple ad groups, which are multiple ads in a campaign that share similar targets. This approach is more cost-effective than putting every single keyword into one ad, which can be expensive.
- Design and test landing page. Every ad must link to a landing page where the product sits. It is a good idea to create a landing page that uses important keywords and provides a good UX. A/B testing can be used to optimize metrics such as revenue per page and average order value.
- Create the ad. The next step is to create an ad for an ad group based on the keyword and competitor research.
- Make a bid. Once an ad is created, a bid is entered into a search engine auction.
- Monitor the campaign. The final step is monitoring the ad's performance with analytics tools, such as Google Analytics. These tools let organizations track the performance of keywords and make modifications to the ad, the keywords used or other elements of the campaign.

Search engine marketing is one of the most effective strategies to reach potential customers. Learn how data analytics can improve content management strategies.






