Microsoft SharePoint
What is Microsoft SharePoint and what is it used for?
Microsoft SharePoint is a document management and collaboration platform that helps a company manage archives, documents, reports and other content that is vital to its business processes. SharePoint's enterprise content management capabilities are helpful to organizations in all industries and in any department within an organization.
SharePoint is configured using a web browser. It provides most of its capabilities via a web user interface (UI) and web applications. SharePoint is used to manipulate content and site structure, create and delete sites, enable and disable product features, configure basic workflows and manage analytics.
New and updated SharePoint features
SharePoint 2019 is the latest version of the application. SharePoint is part of the Office 365 suite, where it is known as SharePoint Online. Microsoft also offers an on-premises version for organizations that prefer to keep their data in-house for compliance or security reasons.
Notable features in SharePoint include:
- Business intelligence (BI). SharePoint 2019 is integrated with Microsoft Power BI, providing access to BI
- Compliance. SharePoint's In-Place Hold Policy Center and Compliance Policy Center let a company's central administration build and apply policies. Users can delete documents from OneDrive for Business sites.
- Document library accessibility. SharePoint provides page landmarks for easy navigation, keyboard shortcuts for various tasks, updates on upload progress, improved callout readings and updates for help documentation.
- Expanded file names. Support is available for file names with special characters, leading with dots and longer than 128 characters.
- Folder sharing. Users can see who is sharing a folder and can invite participants and approve or deny access requests.
- Better integration with Office 365 tools and services, including Microsoft Sway.
- Information rights management. Digital rights management capabilities protect sensitive information and intellectual property from unauthorized access.
- Large file support. There is no limit on file size. However, Microsoft recommends a 10 GB maximum. There is a 250 GB maximum file upload limit.
- MinRole. Administrators can install only the roles they want on SharePoint servers.
- Mobile experience. A touch-friendly mobile interface has been added, giving users a more modern experience. It's easy to switch from mobile view to PC view.
- Navigation UI. SharePoint includes megamenus that render and display on desktop and mobile versions of the platform to enhance site navigation. Developers can natively deliver shortcuts to webpages in SharePoint.
- Project server. Project managers can request resources from other resource managers and use a heat map function to see where resources spend time. They can also create multiple timelines. The project server has improved backup and restoration capabilities.
- Project Syntex. SharePoint integrates with Microsoft intelligent search to help employees locate relevant metadata in emails, presentations and other Office services. Syntex uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate content processing and turn content into knowledge.
- Security. SharePoint 2019 includes coauthoring and autosave features for encrypted documents, information barriers and automatic expiration of external access.
- Site page pinning. Users can pin sites to follow them when on premises or through Office 365.
- Team sites. These are locations where teams can work on projects and share information from anywhere. A team site includes a group of related webpages, as well as a default document library for files, lists for data management and web parts that are customizable.
- Yammer. The Yammer social networking platform has customizable social feeds that let employees interact in the SharePoint environment.
Deprecated Microsoft SharePoint features
SharePoint 2016 was focused on traditional document management. With SharePoint 2019, Microsoft eliminated some collaboration, social media and enterprise search functions that are now included in Office 365. Those functions include the following:
- Delve. A data visualization and discovery tool that incorporates elements of social networking and machine learning with the search capabilities of the Office 365 suite.
- Office Graph. A back-end tool in the Office 365 Suite that facilitates search across integrated applications and applies machine learning to organizational interactions and content use.
- Sway. A presentation tool in the Office suite.
- Teams. A work collaboration tool that allows employees to interact on a working document wherever they are.
- Yammer. A private microblogging and collaboration platform for enterprise social networking.
Microsoft is focusing much of its development roadmap on SharePoint Online. However, it will continue to release on-premises versions because customers may have compliance requirements that require maintaining certain data on premises or because they cannot migrate all their data to the cloud.
Other features that were removed from the SharePoint 2016 server include the following:
- Excel services. Excel capabilities are no longer hosted on SharePoint Server. Instead, it is part of Excel Online in Office Online Server.
- Forefront Identity Manager. FIM synchronizes between Active Directory and SharePoint. SharePoint 2016 does not use FIM but instead uses Microsoft Identity Manager 2016 or another third-party tool.
- SharePoint BI capabilities. Power Pivot and Power View for BI features are not deployed in SharePoint 2016. Power Pivot for SharePoint and Power View for SharePoint add-ins can only be deployed with SharePoint 2016 when using SQL Server 2016.
- SharePoint Foundation. SharePoint Foundation is a free edition that provides a secure, web-based collaboration platform. It is not available in SharePoint Server 2016 but is still available in SharePoint 2013.
- Standalone install mode. This feature is no longer available on SharePoint 2016. It has been replaced by the MinRole farm topology.
- Tags and notes. Users can still create new tags and access any existing ones, but Microsoft discouraged using the feature, as it was slated to be removed.
- Work Management Service Application. This application was removed from SharePoint 2016, including My Tasks and other associated Exchange Task Sync features.
The following features were deprecated or removed in SharePoint Server 2019:
- Access Services 2010 and 2013. These will be deprecated but remain supported. Microsoft recommends exploring Microsoft PowerApps and Power Automate.
- Aggregated newsfeed. This is set to read-only in SharePoint 2019. Microsoft recommends using Teams News, Communication Sites, Yammer or Teams
- Custom help. Microsoft is moving away from its legacy help engine in favor of a new cloud-based customer help tool that is integrated with Office 365.
- Machine Translation Service. This is being deprecated and will no longer be supported. Multilingual communication sites are recommended for users.
- Multi-tenancy. Microsoft removed this function because of the high cost of increasingly complex multi-tenancy implementations of SharePoint on premises.
- PDF reader. The built-in PDF reader function was removed because most web-browsers have their own built-in PDF reading functions.
- Site mailboxes. Site mailboxes will be deprecated but supported. Microsoft recommends customers use the shared mailboxes alternative.
SharePoint 2019 architecture changes and options
SharePoint 2019 includes architectural deployment models that were introduced with SharePoint 2016 as part of Microsoft's move to make SharePoint a cloud-first offering. Microsoft said with SharePoint 2019, it aimed to improve many of the cloud-first technologies introduced in 2016.
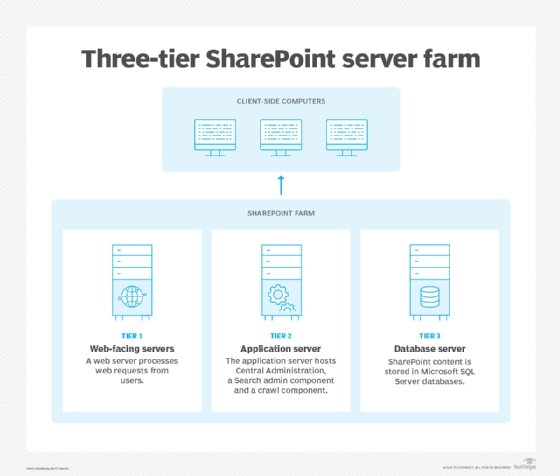
For example, SharePoint 2013 and previous editions relied on service deployments to patch problem servers. SharePoint 2016 had MinRole, a streamlined topology that has a server in a SharePoint farm that runs an explicit set of services based on its role and has no other services turned on. This enables more flexibility, easy fixes and quick updates to each server resulting in faster and more reliable service. SharePoint uses the MinRole farm topology in SharePoint Server 2019 and Online.
At their core, SharePoint's architectural deployment models are largely the same as when they were introduced in 2016. There are four architectural models for SharePoint 2019.
SharePoint Online. SharePoint is delivered using a software-as-a-service subscription model. Microsoft provides updates automatically, but customers are responsible for SharePoint management.
SharePoint on premises. Customers maintain control over all the planning, deployments, maintenance and customizations of their SharePoint environments within their own data centers.
- SharePoint hybrid. This is a combination of a SharePoint Online subscription with an on-premises version of SharePoint. With this approach, customers can meld SharePoint Online services into their overall SharePoint environment while creating a bridge to ultimately migrate SharePoint sites and apps to the cloud.
- SharePoint in Azure. Customers can extend their on-premises SharePoint farms to Microsoft's Azure infrastructure-as-a-service cloud for production, disaster recovery and testing SharePoint Server 2019 environments. This is a version of SharePoint hybrid.
Microsoft SharePoint versions and history
SharePoint has existed in one form or another since 2001. It has grown to more than 200 million users within 250,000 organizations. There have been nine SharePoint versions released since 2001, with SharePoint 2010 Enterprise being the first enterprise-based offering.
Microsoft SharePoint Server 2010 was launched in 2010 with close integration with Microsoft Office and Active Directory. The benefits of SharePoint 2010 included the ability to quickly develop and build websites without programming knowledge. Such websites could be used to manage collaboration tools such as document libraries, discussion boards, shared task lists, shared calendars, blogs, wikis and surveys.
SharePoint 2013 was released as a collaboration platform for customized webpages in November 2012.
The initial release of SharePoint 2013 offered a simplified user experience, as well as new enterprise social media capabilities. Those features expanded upon previously offered capabilities for website management, including shared calendars, blogs, wikis, surveys, document libraries and shared task lists.
SharePoint 2013 also launched with a community forum for users to communicate with each other and categorize discussions. It included a microblogging capability and enhanced search capabilities, as well as e-discovery functionality, claims-based authentication and mobile support. The BI tools in SharePoint 2013 enabled users to organize goals and processes and create customizable data models, reports and dashboards.
SharePoint Server 2016 has the same code as SharePoint Online. As a result, on-premises customers have the same support and performance capabilities for their SharePoint server farms thanks to a few architecture changes.
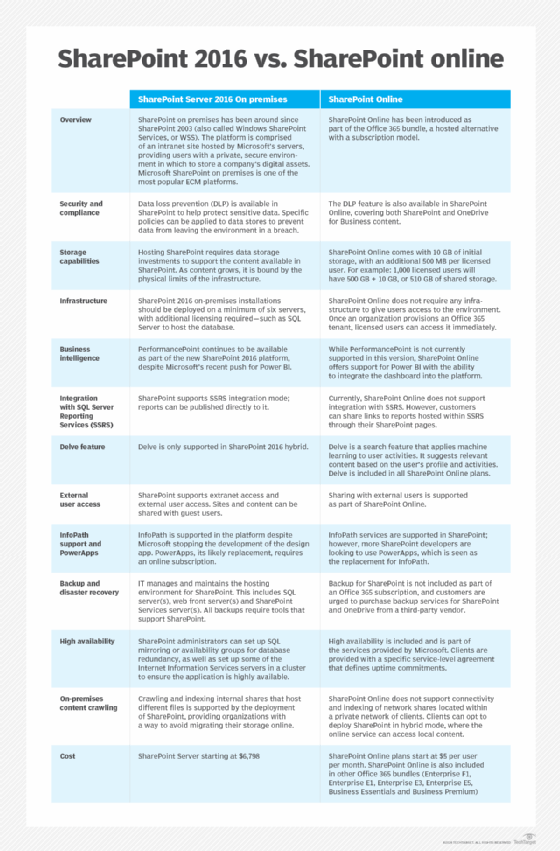
SharePoint 2019 is the latest version. It brings more cloud-based features to the SharePoint Server and hybrid architecture types of the application.
Microsoft SharePoint competitors
While Microsoft SharePoint is a market leader in document collaboration and management, many other cloud-based competitors have entered the market, including Box, DropBox and Google Drive. Beyond document management, the collaboration software industry has grown, with new players gaining traction, including Salesforce Slack and Chatter and Aurea Jive.
In response, in 2017, Microsoft released its own collaboration tool, Teams, to complement SharePoint 2016. Teams is still used in conjunction with SharePoint today. Vendors such as Sitecore, Atlassian Confluence and WordPress all compete with SharePoint in the web content management market.
SharePoint integrates with a number of different collaboration tools. However, some businesses may find alternatives more useful, especially for easier migration to the cloud. Learn 7 alternatives to Microsoft SharePoint.